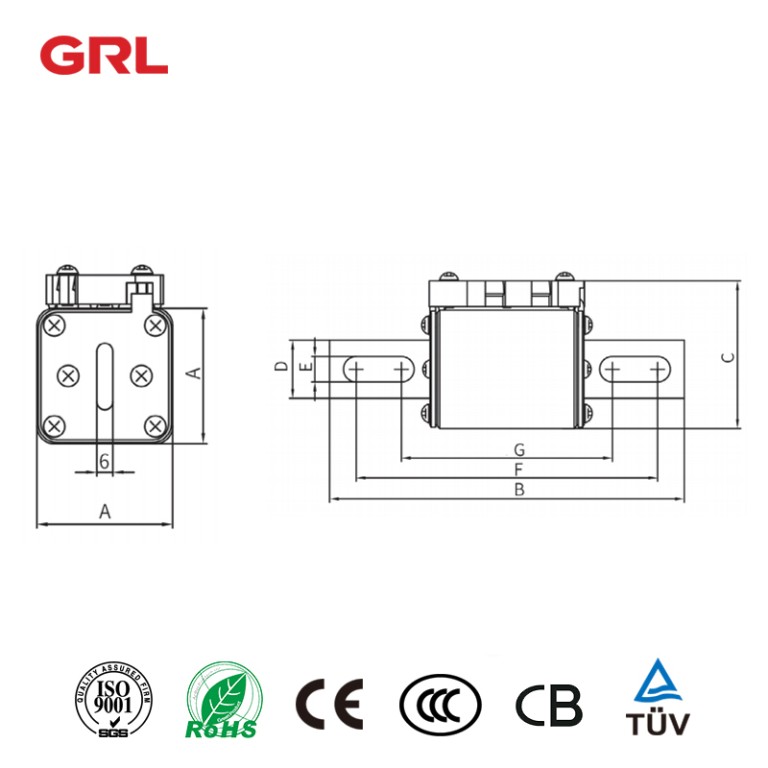
Product description
DNT □ – O1L series semiconductor equipment protection fuse, suitable for AC systems,Rated voltage is 1000V, rated current is 160A~1500A, used as a semiconductor component and the complete set of equipment is used for short-circuit protection.
All performance indicators of the product comply with GB/T 13539.4/IEC 60269-4.
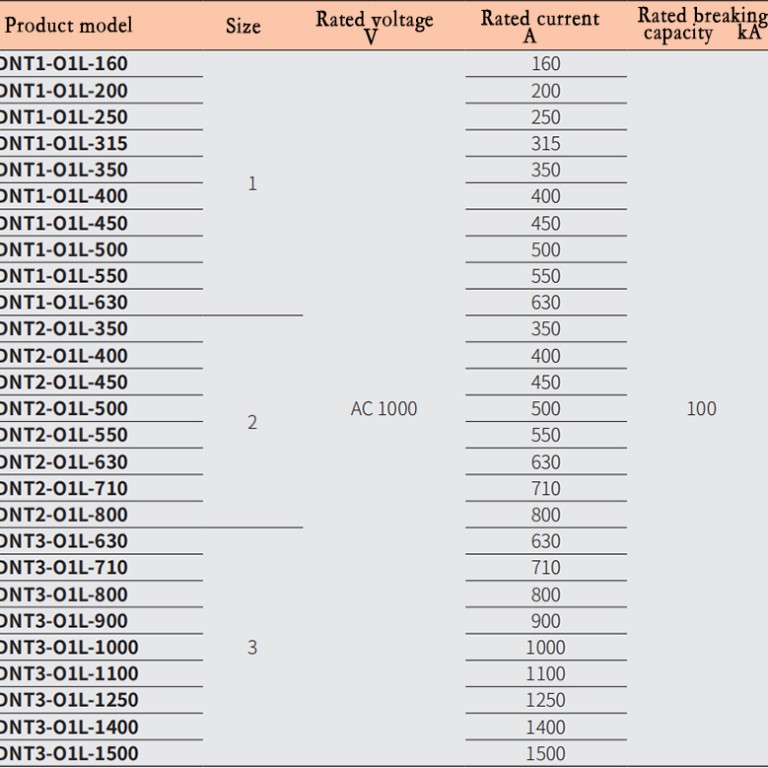
Basic parameters of fuse links
| Product model | size | Rated voltage V | Rated current A | Rated breaking capacity kA |
| DNT1-01L–160 | 1 | AC 1000 | 160 | 100 |
| DNT1-01L–200 | 200 | |||
| DNT1-01L–250 | 250 | |||
| DNT1-01L–315 | 315 | |||
| DNT1-01L–350 | 350 | |||
| DNT1-01L–400 | 400 | |||
| DNT1-01L–450 | 450 | |||
| DNT1-01L–500 | 500 | |||
| DNT1-01L–550 | 550 | |||
| DNT1-01L–630 | 630 | |||
| DNT2-01L–350 | 2 | 350 | ||
| DNT2-01L–400 | 400 | |||
| DNT2-01L–450 | 450 | |||
| DNT2-01L–500 | 500 | |||
| DNT2-01L–550 | 550 | |||
| DNT2-01L–630 | 630 | |||
| DNT2-01L–710 | 710 | |||
| DNT2-01L–800 | 800 | |||
| DNT3-01L–630 | 3 | 630 | ||
| DNT3-01L–710 | 710 | |||
| DNT3-01L–800 | 800 | |||
| DNT3-01L–900 | 900 | |||
| DNT3-01L–1000 | 1000 | |||
| DNT3-01L–1100 | 1100 | |||
| DNT3-01L–1250 | 1250 | |||
| DNT3-01L–1400 | 1400 | |||
| DNT3-01L–1500 | 1500 |
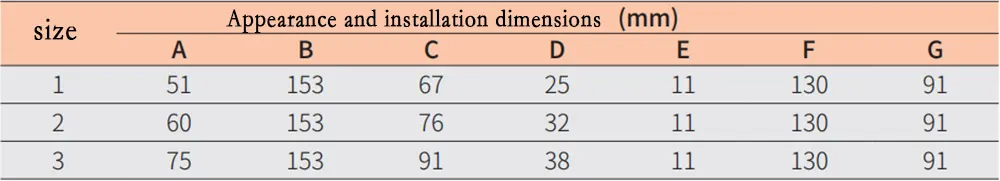
Appearance and installation dimensions
Semiconductor fuses, also known as solid-state fuses or electronic fuses, are specialized devices designed to protect sensitive electronic circuits from overcurrent conditions. They differ from traditional fuses, which rely on a wire or metal strip that physically melts to break the circuit. Semiconductor fuses, on the other hand, use semiconductor devices to rapidly open the circuit when overcurrent conditions are detected.
1.Operation Principle:
Semiconductor fuses operate based on the principle of “current limiting.” When an overcurrent condition occurs, the fuse rapidly increases its resistance, limiting the current flow and protecting the circuit.
2.Types of Semiconductor Fuses:
Resistor-Based Fuses: These fuses use a resistor element that increases in resistance when subjected to high currents. This increase in resistance protects the circuit by limiting the current flow.
Thermal Cutoffs (TCOs): Also known as thermal fuses, they contain a heat-sensitive element that melts or breaks the circuit when a certain temperature threshold is exceeded. While not technically semiconductors, they serve a similar protective function in electronic circuits.
Polymeric Positive Temperature Coefficient (PPTC) Devices: These are self-resetting fuses that use a polymer-based resistor element. When an overcurrent condition occurs, the polymer heats up and its resistance increases, limiting the current. Once the fault is removed, the PPTC device cools down and returns to its low resistance state.
3.Applications:
Semiconductor fuses find widespread use in electronic equipment and devices where protecting sensitive components from overcurrent events is critical. They are commonly found in power supplies, control circuits, motor drives, and telecommunications equipment.
4.Advantages:
Fast Response: Semiconductor fuses have very fast response times, which is crucial for protecting sensitive electronic components.
Precise Current Limiting: They can be designed to provide precise current limiting characteristics, ensuring that the circuit is protected without causing unnecessary disruptions.
5.Selection Criteria:
When selecting a semiconductor fuse, factors like voltage rating, current rating, breaking capacity, and response time must be taken into consideration. Additionally, the fuse should be compatible with the specific application and circuit requirements.
6.Failures and Aging:
Like any electronic component, semiconductor fuses can fail over time due to various factors including aging, thermal stress, and voltage surges. Regular inspection and testing may be necessary to ensure their continued reliability.
7.Replacement:
If a semiconductor fuse is blown or has reached the end of its service life, it should be replaced with a fuse of the same specifications to maintain the circuit’s protection.
how to check semiconductor fuse?
To check a semiconductor fuse, you’ll need a multimeter, which is a versatile tool used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance. Follow these steps:
Safety First: Before you begin, make sure the equipment is disconnected from the power source and ensure you are familiar with electrical safety procedures.
Set the Multimeter: Turn on the multimeter and set it to the “Ohms” (Ω) setting. This is the resistance measurement setting.
Test Leads: Insert the red (positive) test lead into the “Ohm” or “Ω” jack, and the black (negative) test lead into the “COM” or “Common” jack on the multimeter.
Fuse Removal (Optional): Depending on the circuit, you may need to remove the fuse for testing. If so, ensure the equipment is safely disconnected from any power source before removing the fuse.
Testing the Fuse:
a. Place the multimeter leads on each end of the fuse. It doesn’t matter which lead goes where since a fuse is not polarized.
b. If the fuse is intact (i.e., not blown), the multimeter should display a very low resistance reading, typically close to 0 ohms. This indicates that the fuse is allowing current to pass through.
c. If the fuse is blown (open), the multimeter will display an “OL” (Over Limit) reading, indicating infinite resistance. This means there’s a break in the circuit, and the fuse needs to be replaced.
Interpreting the Results:
If you get a low resistance reading, the fuse is likely intact and functioning correctly.
If you get an “OL” reading, the fuse is blown and needs to be replaced.
Reinstallation (If Removed): If you removed the fuse for testing, ensure it is reinstalled correctly before reconnecting the equipment to the power source.
Remember to consult the device’s manual or consult a professional if you are unsure about any step in this process. Additionally, always practice proper safety precautions when working with electrical equipment. If you’re unsure about your abilities or are dealing with a complex electrical system, consider seeking help from a qualified electrician.
Click to view grl group company information>>
Click to view grl fuse link product>>
Click to view fuse base product>>
Click to view fuse holder product>>
leave your question
Get your Comfortable Solution
![]()
GRL Electric Co., Ltd. is one of the leading companies in the Middle And High End market of low-voltage electric in China