NGT2-1000 Semiconductor protection fuse link
Basic parameters of fuse link

Remarks: ● indicates that it has been certified
○ Indicates that the current specification is only applicable to AC400V and AC690V
Basic parameters of fuse link

Remarks: ● indicates that it has been certified
○ Indicates that the current specification is only applicable to AC400V and AC690V
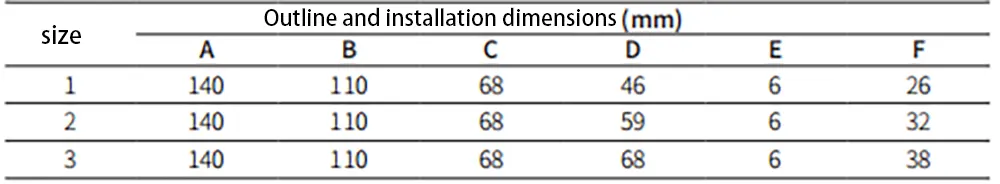
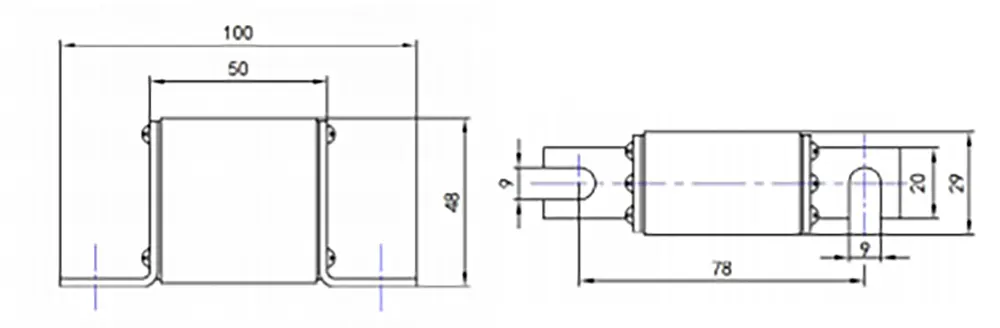
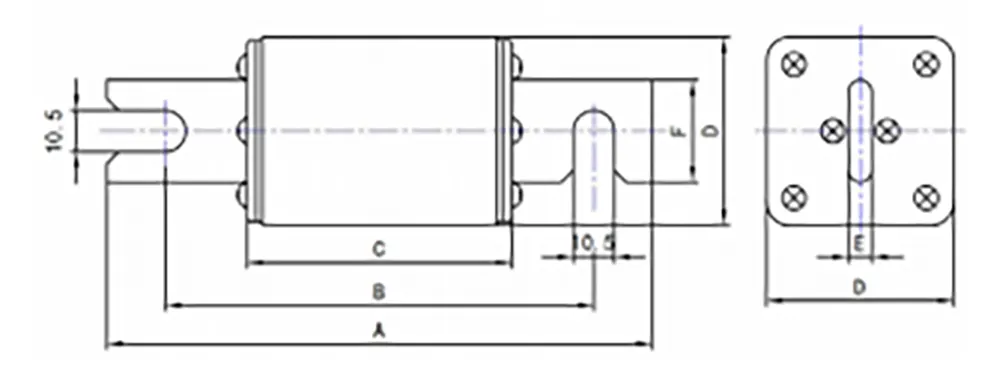
Outline and installation dimensions
Click to view grl group company information>>
Click to view grl fuse link product>>
Click to view fuse base product>>
Click to view fuse holder product>>
Fuse is an electrical component that is designed to protect circuits from overloading and short circuits. The fuse is a simple device that contains a metal wire or filament, which melts when it is exposed to an excessive amount of current. This action causes the circuit to break, thereby protecting other components from damage.
The concept of fuses is not new; they have been around for centuries. In fact, the earliest known fuses were made of hemp or rope that was soaked in resin or tar. When ignited, the rope would burn slowly, providing a time delay before the circuit was broken.Semiconductor protection fuse link
Today, fuses are made of a variety of materials, including glass, ceramic, and plastic. They are commonly used in a wide range of electronic devices, from household appliances to industrial equipment.Semiconductor protection fuse link
There are several different types of fuses available, each designed for specific applications. The most common types of fuses include:
1.Cartridge Fuses – These fuses are cylindrical in shape and are designed to be inserted into a holder. They are commonly used in automobiles, as well as in industrial equipment.
2.Blade Fuses – Also known as spade fuses, these are rectangular in shape and have two prongs that are inserted into a fuse holder. They are commonly used in automobiles and boats.
3.Glass Fuses – These fuses are made of glass and have metal caps on both ends. They are commonly used in household appliances, such as televisions and stereos.
4.Ceramic Fuses – These fuses are made of ceramic and are commonly used in industrial equipment.
5.Thermal Fuses – These fuses are designed to protect against overheating. They contain a special alloy that melts when it reaches a specific temperature, thereby breaking the circuit.
6.Resettable Fuses – Also known as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PPTC) fuses, these fuses are designed to reset themselves after they have been tripped. They are commonly used in electronic devices, such as computers and printers.
7.Automotive Fuses – These fuses are designed specifically for use in automobiles. They are commonly available in blade and cartridge formats.
Fuses are rated based on their current-carrying capacity, which is measured in amperes (A). The rating of a fuse is determined by the maximum amount of current that it can carry continuously without tripping.Semiconductor protection fuse link
In addition to current ratings, fuses also have voltage ratings, which indicate the maximum voltage that the fuse can safely handle. It is important to select a fuse with the correct voltage rating for the application to avoid the risk of electrical arcing.Semiconductor protection fuse link
The basic function of a fuse is to protect against overcurrent conditions. When too much current flows through a circuit, the fuse wire heats up and melts, causing the circuit to break. This action protects the circuit from further damage and prevents potential fire hazards.
The time it takes for a fuse to blow depends on the amount of current flowing through the circuit. A higher current will cause the fuse to blow faster than a lower current.
When a fuse blows, it must be replaced before the circuit can be used again. It is important to replace the fuse with the correct type and rating to ensure proper protection.
The use of fuses offers several advantages, including:
1.Inexpensive – Fuses are relatively inexpensive, making them a cost-effective means of protecting circuits.
2.Reliable – Fuses are a reliable means of protecting circuits, as they do not rely on mechanical or electronic components.Semiconductor protection fuse link
3.Quick Response – Fuses respond quickly to overcurrent conditions, protecting circuits before damage can occur.
However, there are also some disadvantages to the use of fuses, including:1.Limited
leave your question
![]()
GRL Electric Co., Ltd. is one of the leading companies in the Middle And High End market of low-voltage electric in China
